
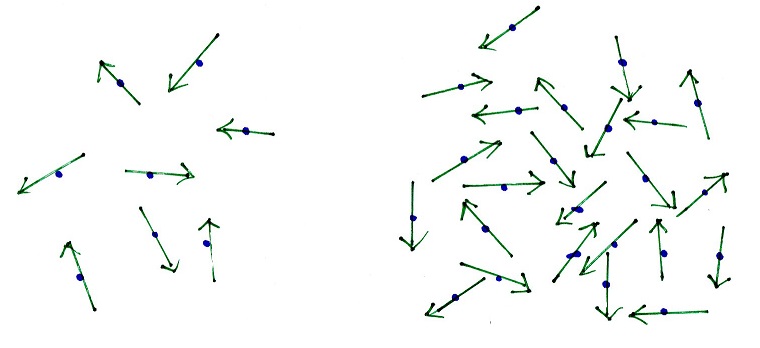
Figure: Microscopic interpretation of the gas pressure These impact forces can be clearly felt when, the cylinder is closed with a piston. If, for example, a gas under high pressure is enclosed in a cylinder, the particles contained in it collide constantly with the cylinder wall and exert forces. The pressure in gases is caused on a microscopic level by collisions of the particles contained therein, which collide with adjacent surfaces and thus exert impact forces! the wall of a container), they exert forces similar to tennis balls thrown against a racket. If the gas particles collide with a surface (e.g. The macroscopically measurable gas pressure (“force per unit of surface area”) can be explained at a microscopic level by means of collisions. In the article “ Gas pressure“, the formation of the gas pressure has already been explained in detail using the particle model. Microscopic interpretation of the gas pressure Formation of the gas pressure the influence of gravity on the molecules is neglected). they have no preferred direction and are therefore statistically distributed in space (i.e. all gas particles move completely randomly, i.e.collisions between gas particles are completely elastic as well as collisions between molecules and surfaces (i.e.the gas particles do not exert any binding forces on each other,.the gas particles are considered as mass points,.First, it is assumed that the gases are ideal gases. In order to develop a model of the behaviour of gas particles, some assumptions must first be made about the properties of gases or the molecules they contain. particle velocity, mean kinetic energy, number of particles, partial mass, etc.)! Assumptions temperature, pressure, volume, gas mass, etc.) and microscopic variables (e.g. With its help it is possible, for example, to deduce the temperature or the pressure of a gas from the mean kinetic energy of the molecules.įor (ideal) gases, the kinetic theory of gases provides important relationships between macroscopically measurable state variables (e.g. In order to connect the macroscopically observed state variables of a gas such as temperature, volume and pressure with the microscopic variables such as particle mass and particle velocity, the kinetic theory of gases was developed. 4 Microscopic interpretation of temperature.3.4 Relation between the motion in x-direction and the total motion.3.2 Variables influencing the gas pressure.3 Microscopic interpretation of the gas pressure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
